We understand the immense effort students invest in mastering their craft. AT GENTLE TOUCH SONO, our goal is to ensure this dedication translates into career success.
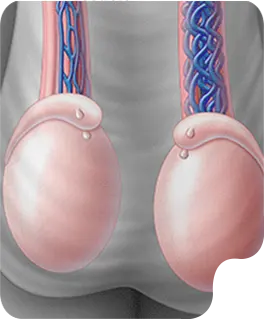
LEFT TESTICLE
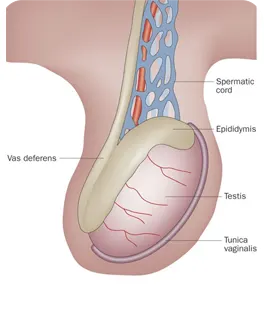
The left testicle is the other primary male reproductive gland, situated within the scrotal sac, where it produces sperm and testosterone. Ultrasound imaging of the left testicle is essential for evaluating its overall health, detection conditions like swelling, infection, or the presence of lesions.
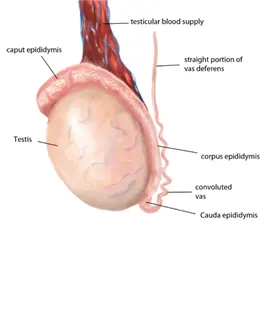
RIGHT EPIDIDYMAL BODY
The right epididymis body is the central, elongated portion of the epididymis running along the posterior aspect of the right testicle. Ultrasound allows for detailed assessment of this segment, looking for signs of epididymitis, epididymis cysts, or other inflammatory changes.
LEFT EPIDIDYMAL HEAD
The left epididymis head is located at the top of the epididymitis Associated with he left testicle, serving s the initial collection point for sperm. Ultrasound examination of the left epididymis head is performed to detect issues such as epididymitis, hydroceles, or other palpable masses.
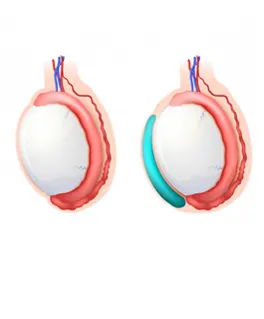
LEFT DOPPLER OF THE TESTICLE
Doppler ultrasound of the left testicle assesses the blood Flow dynamics within the left testicular parenchyma and surrounding vessels. It is invaluable for detecting conditions such as left testicular torsion, where blood flow is acutely absent or diminished, or for identifying varicose veins(varicocele) impacting the left pumping form plexus.
RIGHT TESTICLE
The right testicle is one of the to male productive glands located within the scoutmaster responsible for producing sperm a male hormones. Ultrasound provides detailed images to assess its size, internal texture, and any potential abnormalities such as cysts, masses, or signs of inflammation.
LEFT EPIDIDYMAL BODY
The left epididymis body extends along the back surface of the left testicle, serving as a conduit and storage area for maturing sperm. Ultrasound of the left epididymis body helps identify pathologies like inflammation, benign cystic formations, or abnormalities causing scrotal pain.
RIGHT EPIDIDYMAL HEAD
The right epididymis head is the uppermost part of the coiled The right epididymis head is the uppermost part of the coiled tube(epididymis) positioned on the superior aspect of the right testicle. Ultrasound helps visualize this structure to identify any fluid collection, inflammation (epididymitis), or small cysts.
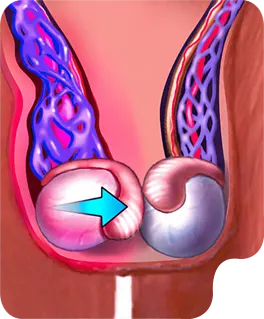
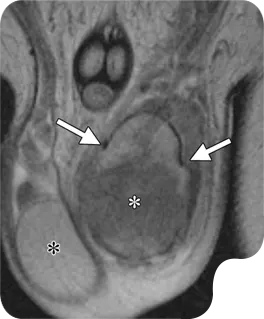
SCROTAL/TESTICULAR
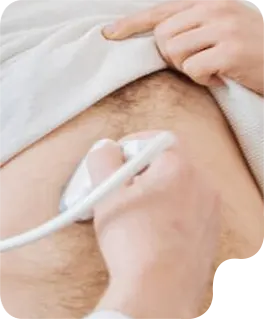
This ultrasound examination focuses on the scrotum, the sac that contains the testicles, epididymis, and the spermatic cord. It is used to evaluate for abuses of course pain, swelling, or masses, such as testicular torsion, epididymitis, o hydroceles. Doppler imaging can be added to assess blood flow within the testicles, which is crucial in cases of suspected torsion.