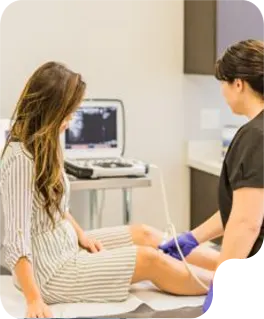
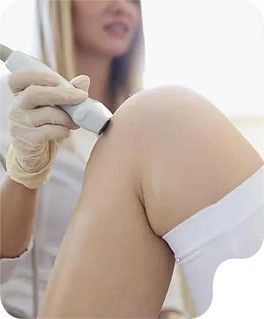
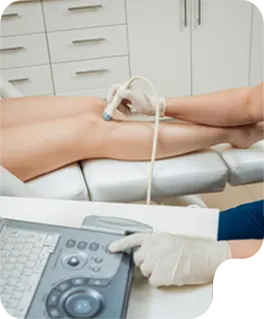
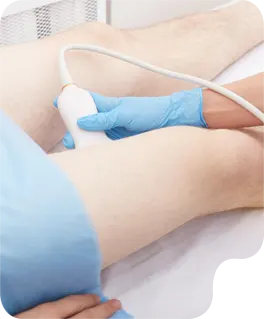
We understand the immense effort students invest in mastering their craft. AT GENTLE TOUCH SONO, our goal is to ensure this dedication translates into career success.
Lower Extremity Doppler
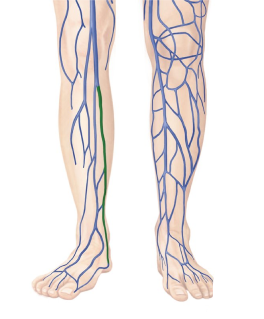
This ultrasound technique evaluates the veins in the legs to detect blood clots (deep vein thrombosis or DVT) and assess for venous insufficiency. Doppler imaging is used to visualize blood flow direction and velocity within the veins. This study is crucial in diagnosing the cause of leg pain, swelling, or discoloration and preventing potentially serious complications.
Peroneal Veins
The peroneal Veins are deep veins situated in the lateral compartment of the lower leg, responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the muscles and tissues of that area. These veins typically run alongside the peroneal artery and ultimately drain not the tibia-peroneal trunk, contributing to the popliteal venous system. Assessment of the peroneal veins is important for detecting deep vein thrombosis, particularly in the distal calf.
cfv/gsv
The Common Femoral Vein(CFV) is a large, deep vein in the groin that collects deoxygenated blood from the entire lower limb. I serves as a critical junction where the superficial venous system, primarily via the Great Saphenous Vein (GSV), connects with the deep system. Ultrasound assessment of this confluence is essential for detecting deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and evaluating the competency of the saphenofemoral valve, which is crucial in diagnosing venous insufficiency.
Superficial Femoral Vein (Proximal, Mid, Distal)
Superficial Fermoral Vein, despite its name, is a major deep vein traversing the length of the thigh, responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the deep tissues of the upper leg. It is typically evaluated in proximal, mid, and distal segments is vital for identifying the presence and extent of deep vein thrombosis, a common and potentially serious condition.
Upper Extremity Doppler
Similar to the lower extremity venous Doppler, this exam focuses on the veins and sometimes Arteries of the arm. It is used identify blood clots, assess for venous or arterial insufficiency, and evaluate the latency of dialysis access grafts or fistulas. Doppler technology allows for the visualization and measurement of blood flow in these vessels. You will be able to see in REAL-TIME imaging.
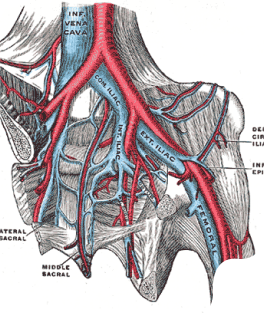
Common Iliac Vein
The Common Iliac Vein is a large, central vein formed by the confluence of the external And internal iliac veins, representing a major conduit for deoxygenated blood from the entire lower extremity and pelvic region. Located within the pelvis, it ascends to join the contralaeral common iliac vein, forming the inferior vena cava. Ultrasound assessment of the common iliac vein is crucial for detecting more proximal deep vein thrombosis, which can significantly impact venous return from the lower limbs.
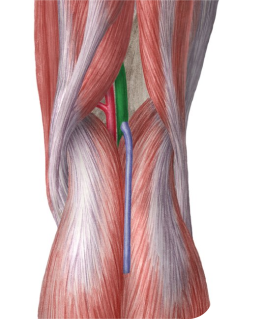
Popliteal Vein
The Popliteal vein is a key deep vein located behind the knee, serving as a continuation of the superficial femoral vein and collecting blood from the calf veins. This vessel plays a critical role in draining deoxygenated blood from the entire lower leg and foot back towards the heart. Ultrasound imaging of the popliteal vein is indispensable for diagnosing deep vein thrombosis in the popliteal fossa and evaluating for venous insufficiency in this region.
Posterior Tibial Vein
The Posterior Tibial Veins are the primary deep veins in the posterior compartment of the lower le, draining deoxygenated blood from the calf muscles, sole of the foot, and ankle. These veins ascend behind the tibia, eventually joining with the anterior tibial veins to form the popliteal vein. Doppler evaluation of the posterior tibial veins is frequently performed to identify deep vein thrombosis, a common site for clot formation in the lower extremity.